Inside the 2026 Quantum Financial System: How It Could Break Traditional Banking Fees
Blockchain
December 10, 2025
Copy link
Dimpal Kumar
Co-Founder

Table of contents
Table of contents
Most people aren’t losing money because they are “bad with money” – they are losing it inside a financial system that still behaves like it is 1975. In 2024, the average cost of a cross‑border payment was about 6.4% in fees, and a typical SWIFT transfer could still take 3–5 days to fully settle, especially for smaller businesses and retail users.
For a worker sending 500 dollars home, that fee alone can erase more than 30 dollars before the money even arrives.
At the same time, a new risk is forming on the horizon: quantum computers powerful enough to break today’s encryption. In a recent enterprise survey, 69% of organizations said they recognize the threat quantum computing poses to current cryptography, but only about 5% have actually implemented quantum‑safe protections so far and 95% are still lack.
Central banks and regulators are already urging financial institutions to start preparing, warning that critical data encrypted today could be decrypted in the future if systems do not transition in time.
This is exactly why the Quantum Financial System (QFS) is gaining global attention.
QFS aims to fix the two biggest failures of traditional finance:
✔ Slow, costly money movement
✔ Outdated cryptography vulnerable to future quantum attacks
Instead of just upgrading SWIFT messages, QFS proposals combine instant or near‑instant settlement, distributed ledgers, and quantum‑safe cryptography to move value with lower friction and higher resilience against future attacks. Analysts expect quantum‑focused financial technologies to grow rapidly, with the quantum finance market projected to reach several billion dollars by 2030 as banks and fintechs race to harden their infrastructure
This guide explains exactly what the Quantum Financial System means for your financial future. You’ll discover how QFS compares to both traditional banking and blockchain technology, which cryptocurrencies are preparing for the quantum era, and most importantly-how to position yourself for this seismic shift in global finance.
The Quantum Financial System (often called QFS) refers to a proposed next-generation financial infrastructure that uses quantum computing technology to process transactions, secure data, and manage digital assets with capabilities far beyond what traditional computers can achieve.
Think of it this way: If traditional banking systems are like bicycles and blockchain is like a motorcycle, then QFS is like a supersonic jet. It operates on fundamentally different principles that unlock previously impossible levels of speed, security, and efficiency.
The quantum financial system combines three revolutionary elements:
The QFS meaning goes beyond just faster transactions. It represents a fundamental shift in how financial trust is established. Instead of relying on central authorities like the Federal Reserve or commercial banks to verify transactions, the QFS banking system uses quantum-verified cryptographic proofs that are mathematically impossible to forge or manipulate.
The QFS is not owned by a single government or bank; it is the result of collaborations between quantum technology companies, financial institutions, blockchain development projects, and policy groups working on “quantum-ready” finance.
Over recent years, major consortia have run pilots and trials to standardize quantum financial protocols, leading up to live implementations of quantum-enabled systems in 2025-2026.
This ecosystem includes:
Together, these players form the broader QFS landscape, even if different regions or networks brand their solutions differently.
Traditional banking cannot survive the quantum era without upgrading. Why? Because quantum computers can break the encryption that protects banks today. Here is the more detailed breakdown why quantum banking system wins in 2026:
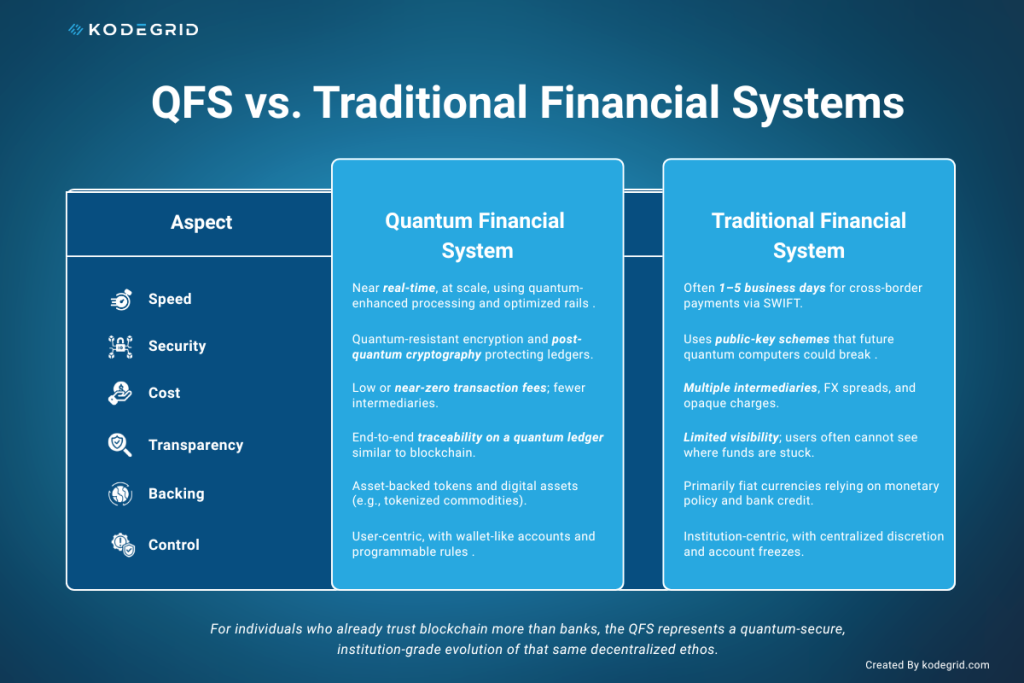
QFS is designed to fix precisely what legacy systems get wrong: speed, transparency, cost, and security. Traditional cross-border payments can take days, depend on chains of intermediaries, and suffer from opaque fees and compliance delays. QFS seeks to make settlement real-time, fully traceable, and cryptographically secure, with transaction costs driven close to zero.
For individuals who already trust blockchain more than banks, the QFS represents a quantum-secure, institution-grade evolution of that same decentralized ethos.
The quantum banking system isn’t built on a single breakthrough-it’s an architectural framework combining multiple quantum technologies.
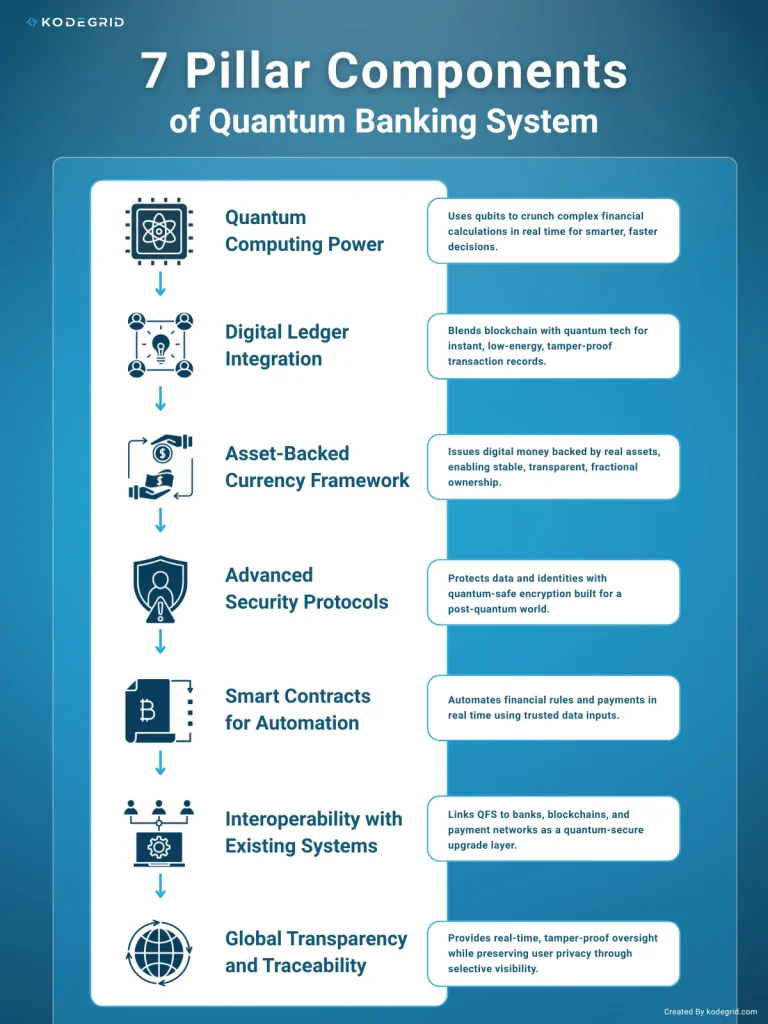
To understand how the QFS banking system works, we need to break down its seven components:
Quantum computers use qubits, which can represent many states at once, to explore huge solution spaces in parallel instead of step by step like classical machines. This turns “impossible” financial calculations into real‑time tools.
This means:
For QFS users, the result is smarter risk management, more accurate pricing, and financial decisions that react instantly to market changes-not hours or days later.
The QFS ledger combines distributed ledger technology with quantum concepts to overcome traditional blockchain limits around speed and energy use.
Key upgrades:
Where classic chains rely on redundancy and computation for security, a QFS‑style ledger leans on the laws of quantum mechanics, unlocking much higher throughput with lower energy and stronger integrity.
The QFS monetary system is designed around digital assets that are backed by real‑world value, not just trust in a central bank. Quantum tech makes continuous verification and valuation practical.
Core ideas:
This model aims to give users stability and transparency: currencies that are both asset‑backed and verifiably backed at all times.
Traditional finance relies on math problems that are hard for current computers but vulnerable to future quantum attacks. QFS security is built around quantum‑safe and quantum‑native methods from day one.
Security stack highlights:
Instead of “hoping” current ciphers last, QFS‑style designs treat quantum threats as a baseline and build infrastructure that is secure in a post‑quantum world.
Smart contracts in QFS keep the “if this, then that” logic of blockchain, but gain more data, more speed, and more intelligence.
QFS smart contracts can:
This turns QFS into an automation engine for finance: that closes instantly when conditions are met, loans that reprice fairly in real time, and supply‑chain payments that release the moment delivery is verified.
QFS is designed to run alongside traditional and blockchain systems and gradually take over high‑value or high‑risk functions first.
Interoperability looks like:
For users and institutions, this means you do not lose access to old rails immediately; QFS becomes a faster, safer upgrade path rather than a forced jump.
The QFS aims for “transparent privacy”: regulators and systems can see what they need to manage risk and crime, while individuals keep control over their personal data.
Key elements:
This gives the QFS banking system real‑time, tamper‑proof auditability and powerful anti‑crime tools, without turning every transaction into fully public data.
Let’s walk through exactly what happens when you send money using the quantum financial system, comparing it to traditional banking and blockchain to highlight the differences.
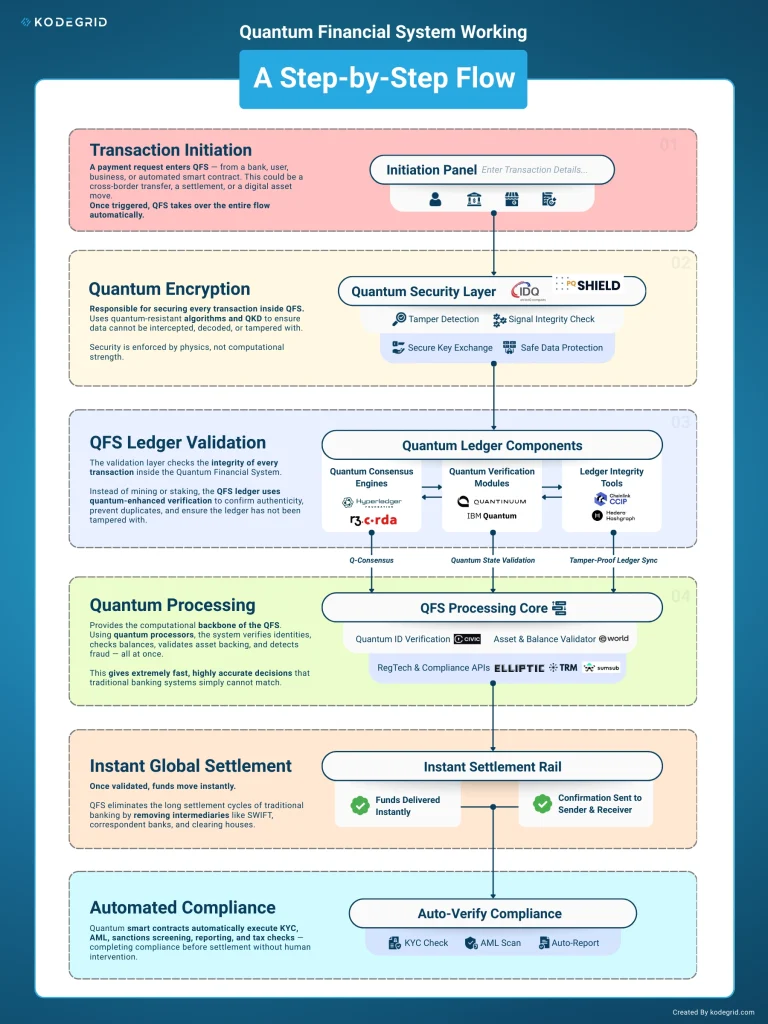
The Quantum Financial System transforms the entire flow of money into a frictionless, automated, and tamper-proof process. Instead of relying on slow banking rails, human verification, and outdated encryption, QFS processes every transaction through quantum encryption, real-time ledger validation, and automated compliance checks.
This means payments-whether domestic or cross-border-are settled instantly with near-zero fees and with a level of security traditional banking simply cannot match. Every action inside QFS is verified at the physics level, making fraud or tampering not just difficult but scientifically impossible.
Several capabilities distinguish QFS-style architectures from both legacy banking and standard crypto networks. These features represent not just incremental improvements, but fundamental reimagining of how financial systems can operate when powered by quantum technology.

QFS implementations adopt post‑quantum cryptography and quantum‑safe key management so they remain secure even when large‑scale quantum computers arrive, while today’s RSA and ECC‑based systems are known to be vulnerable to future quantum attacks.
For banks and users, this shifts security from “hope current encryption holds” to “designed to survive quantum decryption,” reducing the risk of long‑term data and value theft.
Instead of focusing mainly on speculative coins, QFS natively supports tokenized real‑world assets-commodities, treasuries, real estate, private credit, carbon credits, and more-which can be used as collateral, yield‑bearing instruments, or payment media.
This means QFS money and QFS coins can directly represent productive, real‑economy value, enabling things like fractional property ownership, tokenized funds, and on‑chain financing for businesses rather than only trading meme assets.
QFS infrastructure is built for very high transaction volumes and near‑instant finality, using quantum‑enhanced computation and optimized ledger designs to avoid congestion and fee spikes.
Where traditional rails settle in T+1 to T+3 and many chains slow down or become expensive under load, QFS aims for continuous, 24/7 settlement with predictable costs, making it suitable for institutional payments, securities settlement, and high‑volume retail use.
Smart contracts and automated workflows in QFS turn money into an intelligent tool: payments can be conditional, time‑locked, risk‑adjusted, or portfolio‑aware by design. At the same time, embedded compliance checks (KYC/AML rules, sanctions screening, tax logic) can run automatically at transaction time, reducing manual reviews and making it easier for institutions to meet regulatory requirements without sacrificing user experience.
Rather than existing in a silo, QFS initiatives are being architected to connect with both legacy finance (SWIFT, ACH, traditional banks) and blockchain ecosystems (public and permissioned chains).
This “bridge‑first” mindset allows gradual migration: high‑value flows and sensitive data can move onto quantum‑safe rails first, while users and institutions still interact with familiar interfaces and assets during the transition.
Cryptocurrencies fit naturally into QFS because they’re already digital, decentralized, programmable, and built on ledger technology – all core components of quantum financial architecture.
However…The challenge Most existing cryptocurrencies were built using classical cryptography, such as:
These algorithms are strong today, but a sufficiently powerful quantum computer could theoretically break them using Shor’s algorithm, exposing vulnerabilities in wallets and signatures.
This is why the crypto ecosystem is already transitioning toward Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) – cryptographic methods designed to resist both classical and quantum attacks.
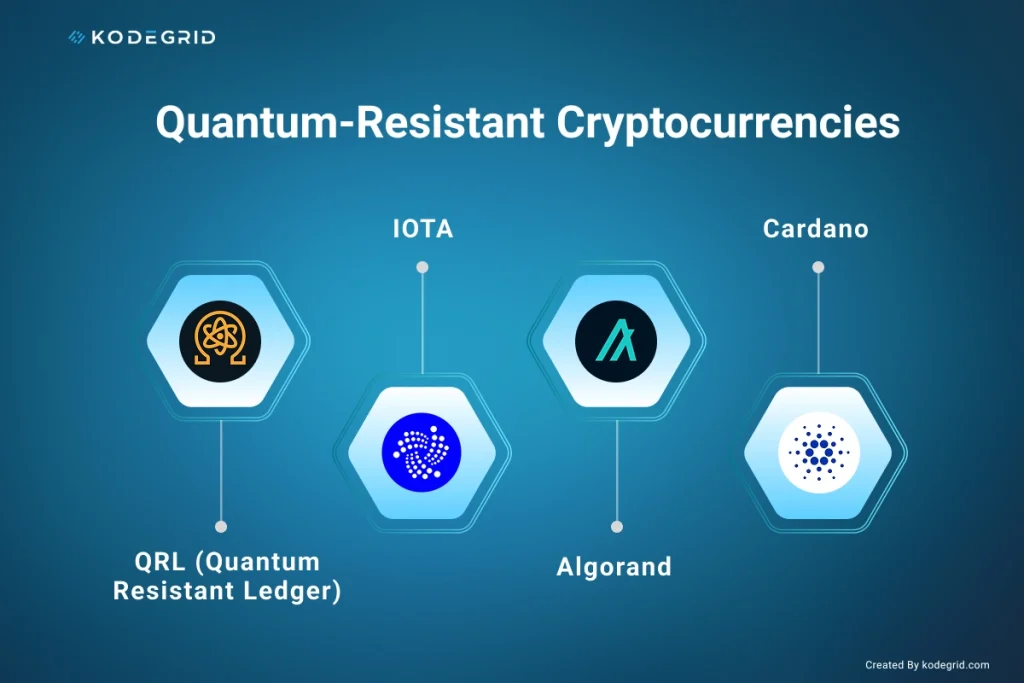
QFS relies heavily on quantum-secure communication and verification, so any cryptocurrency integrated into it must evolve toward quantum-resistant standards.
If we look ahead from 2026 to 2030, the Quantum Financial System isn’t just an upgrade – it represents a complete reset of how global finance functions at every layer. We’re talking about a shift as dramatic as moving from paper mail to the internet. QFS will change how money moves, how identities are verified, how banks communicate, and how nations build their monetary systems.
By 2030, we expect financial institutions to rely heavily on quantum-secure communication channels, real-time settlement networks, and asset-backed digital currencies integrated into a QFS ecosystem. CBDCs will likely run on quantum rails. Identity verification will shift from passwords to quantum-secure digital identities.
Banks will operate hybrid cloud–quantum infrastructures. And global settlements – which currently rely on dozens of intermediaries – will compress from days to milliseconds.
The pain points of today’s banking-slow cross-border payments, opaque fees, and vulnerable encryption-are no longer just annoyances; they are structural risks in a world racing toward powerful quantum computers. The Quantum Financial System addresses these issues by combining quantum technology, distributed ledgers, and asset-backed digital money into a coherent, user-centric architecture.
If you already understand blockchain’s promise and are looking for a system that is faster, more secure, and future-proof, exploring QFS concepts, qfs accounts, and quantum-resistant cryptocurrencies is a practical next step.
As 2026 unfolds, the real question will not be whether quantum finance is coming-but how quickly users and institutions choose to move from legacy rails to quantum-ready networks.